A pre-defined room temperature of 20 C was applied before welding. Emissivity Table for Infrared Thermometer Readings Material Emissivity Value Adobe 090 Alloy.
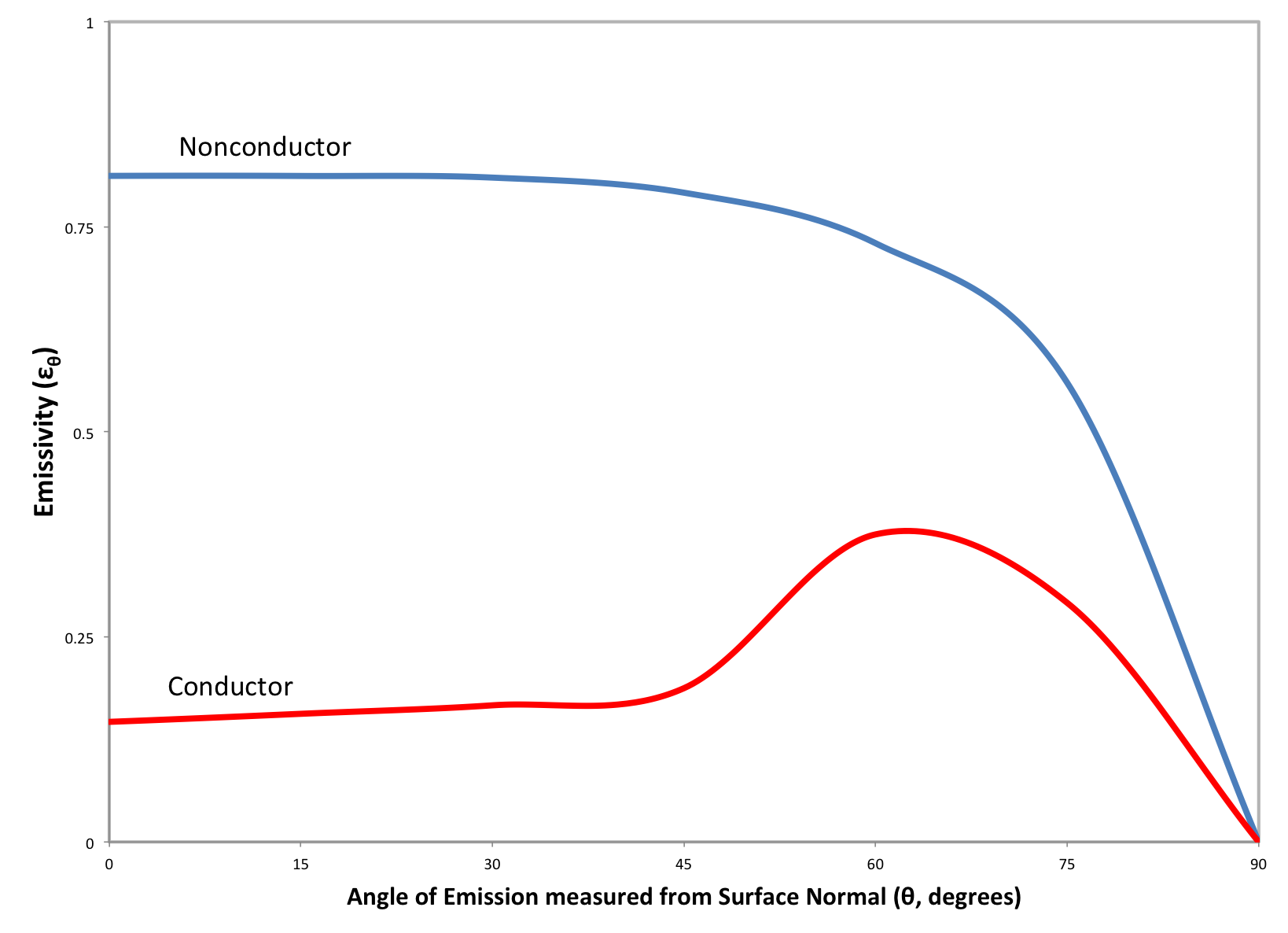
Total Normal Emissivities Of Selected Materials Neutrium
There is much of interest in the possible use of carbon fiber reinforced silicon carbide composite materials for hot structures and thermal protection systems 1 2.
. Sample Sample Emissivity climatic temperature chamber 0C average temperature completely 200 e 0932 165e undoped 25e 0939 lpolytiopbene 300 e 0944 partially 200 e 0906 165e doped 25e 0917 Table 4 Sample Emissivity Emissivity temperature BaTi03 roughAl 0C 5 0937 0143 10 0938 0140. At 1500 K the. This behavior is a consequence of the increase in the free-carrier concentration with the temperature.
220µm over a temperature range from 300 to 900 C at normal incidence. This theory is known to work well for metals at near room temperature and at wavelengths greater than about 10 microns. Further a careful study of the uncertainty components of this measurement.
The total hemispherical emissivity of the specimens was determined from the input electronbeam power densities and the measured temperatures. 20Ni-25Cr-55Fe oxidized 090 - 097 Alloy. However the agreement we found between the hemispherical emissivity obtained by a theory of semi-transparent Silicon and the obtained experimental results makes us believe that the LIGO Voyager test masses because of their dimensions will have effective emissivities around 07 which would be enough to remove about 86 W 75 W for a shield at 60 K 80 K.
For the high-emissivity layer silicon dioxide and silicon nitride also have relatively high absorption coefficient at 95 μm which are approximately 26574 and 9362 cm 1 respectively. Yes Emissivity changes with temperature because of energy that is tied up in the behavior of the molecules that form the surface. The emissivity value follow a linear dependency in the 120-260 K temperature range.
Since the emissivity of a material will vary as a function of temperature and surface finish the values in these tables should be used only as a guide for relative or delta measurements. As the temperature increases the emissivity increases shows a maximum at about 950 K and then starts decreasing. Silicon becomes semitransparent at wavelengths longer than 11 μm 1.
Phonons contribute to emis- of this wafer is negligible at room temperature while at sivity changes. Sample temperature distribution circ C. In this paper we present the temperature-dependent emissivity of a silicon sample estimated from its cool-down curve in a constant low temperature environment 82K.
The total emissivity of a 390μmthick specimen of lightly doped silicon rises from 012 at 280 C to a limiting value of 07 at 650 C. The total emissivity ε for Metals Non-metals and Common Building Materials are given. P The calculated emissivity does not agree with the data taken from 35 to 148 microns and at elevated temperatures.
Tional emissivity of SiC and Pt10Rh are performed in the spectral range of. Air or any non-conducting or weakly conducting. 60Ni-12Cr-28Fe oxidized 082 - 089.
At 155 µm the simulation and experimental data estimated a 4 greater emissivity at 1500 K than at room temperature. Following Plancks law the total energy radiated increases with temperature while the peak of the emission spectrum shifts to shorter wavelengths. However the curves may asymptotically approach the.
The surface of a perfect black body with an emissivity of 1 emits thermal radiation at the rate of approximately 448 watts per square metre at room temperature 25 C 29815 K. The total emissivity of four samples of silicon of different resistivities is measured in the temperature range 880-1550 K. As Nn or N decreases the agreement at room temperature is good only at progressively greater wavelengths.
The room temperature was measured as 213 C. B histogram of temperatures for ATR and emissivity correction methods. The emissivity of silicon was observed in the spectral region from 04 to 15 mu at various temperatures from 340K to 1070K by using two n-type.
The total emissivity of a 390-μm-thick specimen of lightly doped silicon rises from 012 at 280 C to a limiting value of 07 at 650 C. This behavior is a consequence of the increase in the freecarrier concentration with. This result is of great interest to the LIGO Voyager.
In some instances the emissivity measurement of Si meets some challenges at 47 μm because the radiant energy from the heater penetrates the wafer and is detected by the radiometer causing interference. In this paper we present the temperature-dependent emissivity of a silicon sample estimated from its cool-down curve in a constant low temperature environment approx 82K. Emissivity at room temperature is assumed to be applicable at higher temperatures 3.
The emissivity depends on carrier concentration in the silicon samples. After showing a broad minimum at about 1200 K it. The silicon wafer near room temperature is semitransparent at a wavelength more than 11 spl mum which makes emissivity behaviors complicated.
The energy emitted at shorter wavelengths increases more rapidly with temperature. The wavelength region of 12 to 35 microns and at room temperature. The exact emissivity of a material should be determined when.
The emissivity value follow a linear dependency in. Beyond 14 µm ε λincreases with the temperature. The emissivity value follow the linear dependency ϵ T 245 10 3 T 116 10 1 in the 120260 K temperature range.
SEMATECH on the temperature-dependent emissivity of silicon- For RTP pyrometers are the instruments of choice for related materials and structures are presented in this study. Therefore the directional total emissivities measured at elevated temperatures. In this paper we presented the temperature-dependent effective emissivity of a silicon sample estimated from its cool-down curve in a constant low temperature environment 82 K.
This BIPV system consists of an outer amorphous silicon PV laminate. All real objects have emissivities less than 10 and emit radiation at correspondingly lower rates. The ratio varies from 0 to 1.
The band gap of single crystal silicon is 112 eV at room temperature. These results have been acquired using a spectral emissometer.
![]()
Emissivity Of The Bilayer Structure Under Normal Incidence Vs The Download Scientific Diagram

Sato S 1 Spectral Emissivity Of N Si Of Thickness 1770 Mm And Doping Download Scientific Diagram
Total Emissivity Of Low Doped Silicon As A Function Of Temperature Download Scientific Diagram

Room Temperature Emissivity With The Integrated Sphere Measurement Download Scientific Diagram

Comparison Between Spectral Normal Emissivity Of Silica 162 M Thick Download Scientific Diagram

Simulated Results On Emissivity Of 700 Mm N Si On 65 Nm Sio 2 Of Doping Download Scientific Diagram

Results Of Simulation Of Emissivity As Function Of Wavelength For Download Scientific Diagram

Temperature Dependence Of The Normal Spectral Emissivity Of The Sio 2 Download Scientific Diagram
0 comments
Post a Comment